解读:Event-based Stereo Visual Odometry
ESVO 中使用了类似于 SGM 的代价聚合吗?如果有,那么代价聚合的方法是什么?
Event-based Stereo Visual Odometry 提出了一种基于双目事件相机的视觉里程计。 本文之后的部分将 Event-based Stereo Visual Odometry 简写为ESVO.
ESVO 的源码已在 Github 开源,Cpp 实现,运行环境为 ROS.
TODO: Cpp Hpyerthreading
ESVO 主要由三大部分组成,分别是 Event Preprocessing, Mapping, Tracking.
- Event Preprocessing
- 对输入的原始事件流进行滤波,生成 Time-Surface Maps.
- Mapping
- 接收Time-Surface, 进行双目匹配,得到深度,生成 Local Map 与 Point Cloud.
- Tracking
- 对 Local Map 进行跟踪,生成相机的 Pose(6Dof), 将变换矩阵返回给 Mapping 模块
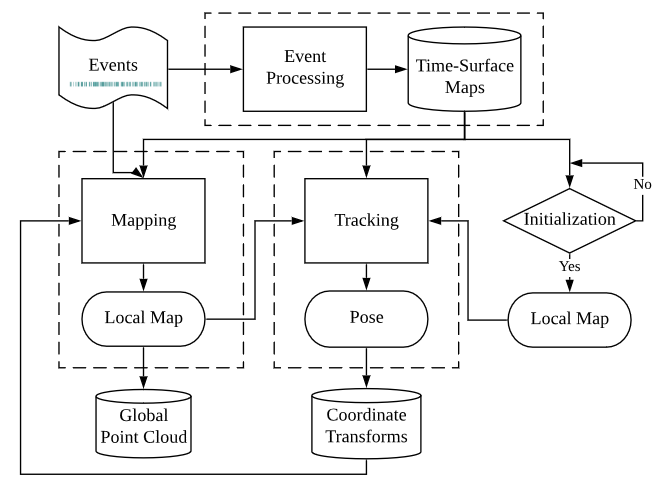 ESVO System Flowchart1
ESVO System Flowchart1
环境配置与编译
该部分将介绍如何安装 ESVO 所需依赖,以及如何编译 ESVO.
这里使用 WSL2+Ubuntu 20.04,预先安装 ROS1以及 catkin build, eigen, pcl
若安装过程中报错,请善用搜索引擎。
Preparation
Create ROS workspace for catkin build
1
2
3
4
5
mkdir -p ~/rosCatkinBuild/src
cd rosCatkinBuild/src
catkin_init_workspace
cd ..
catkin build
Install rpg_dvs_ros
https://github.com/uzh-rpg/rpg_dvs_ros
Clone the repository
1
2
cd ~/rosCatkinBuild/src
git clone https://github.com/HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/ESVO.git
Install yaml-cpp
1
2
3
4
5
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/jbeder/yaml-cpp.git
cd yaml-cpp
mkdir build && cd build && cmake -DYAML_BUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON ..
make -j8
Install dependence
1
2
3
4
5
sudo apt install python3-catkin-tools python3-osrf-pycommon
sudo apt-get install python3-vcstool
cd ~/rosCatkinBuild/src
vcs-import < ESVO/dependencies.yaml
sudo apt-get install autoconf
Fix bug in pcl
编译 ESVO 时报错:
1
2
3
4
5
In file included from /home/yousa/rosCatkinBuild/src/ESVO/esvo_core/src/esvo_Mapping.cpp:13:
/usr/include/pcl-1.10/pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h: In member function ‘std::vector<int> pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT>::getNeighborCentroidIndices(const PointT&, const MatrixXi&) const’:
/usr/include/pcl-1.10/pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h:340:21: error: ‘Index’ is not a member of ‘Eigen’
340 | for (Eigen::Index ni = 0; ni < relative_coordinates.cols (); ni++)
| ^~~~~
1
2
3
4
5
In file included from /home/yousa/rosCatkinBuild/src/ESVO/esvo_core/src/esvo_Mapping.cpp:13:
/usr/include/pcl-1.10/pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h: In member function ‘std::vector<int> pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PCLPointCloud2>::getNeighborCentroidIndices(float, float, float, const MatrixXi&) const’:
/usr/include/pcl-1.10/pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h:670:21: error: ‘Index’ is not a member of ‘Eigen’
670 | for (Eigen::Index ni = 0; ni < relative_coordinates.cols (); ni++)
| ^~~~~
Open /usr/include/pcl-1.10/pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h
1
sudo gedit /usr/include/pcl-1.10/pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h
In line 340 and 670:
1
2
//for (Eigen::Index ni = 0; ni < relative_coordinates.cols (); ni++)
for (int ni = 0; ni < relative_coordinates.cols (); ni++)
Build ESVO
1
2
cd ~/rosCatkinBuild
catkin build esvo_time_surface esvo_core
Run ESVO
Donwload dataset
https://sites.google.com/view/esvo-project-page/home
修改bag文件地址
修改其中hkust_lab.bag 地址,其他launch file同理
1
gedit yousa\rosCatkinBuild\src\ESVO\esvo_time_surface\launch\rosbag_launcher\hkust\hkust_lab.launch
Usage
Remember to source the workspace before running the code.
1
source rosCatkinBuild/devel/setup.zsh
Maybe start roscore first
1
roscore
esvo_time_surface
Fix bug:
stereo_time_surface.launch 最后几行给 rqt 传参有 bug
1
gedit \home\yousa\rosCatkinBuild\src\ESVO\esvo_time_surface\launch\stereo_time_surface.launch
所以去掉这几行,手动在终端中启动 rqt_gui 进行可视化。
1
2
3
<!-- Visualization -->
<node pkg="rqt_gui" type="rqt_gui" name="rqt_gui"
args="--perspective-file $(find esvo_time_surface)/esvo_time_surface.perspective" />
启动 esvo_time_surface 节点,生成 Time-Surface。打开终端,运行以下指令:
1
roslaunch esvo_time_surface stereo_time_surface.launch
To play a bag file, go to esvo_time_surface/launch/rosbag_launcher and modify the path in [bag_name].launch according to where your rosbag file is downloaded. Then execute
1
roslaunch esvo_time_surface [bag_name].launch
e.g.
1
2
3
roslaunch esvo_time_surface system_hkust.launch
roslaunch esvo_time_surface rpg_bin.launch
roslaunch esvo_time_surface upenn_indoor_flying1.launch
esvo_core
esvo_core 实现了论文中提出的 mapping 和 tracking 方法,初始化是在 mapping 部分实现的。这将同时启动两个 esvo_time_surface 节点(分别用于左右事件相机),mapping 节点和 tracking 节点。 运行以下命令启动系统:
1
roslaunch esvo_core system_xxx.launch
e.g.
1
2
3
roslaunch esvo_core system_hkust.launch
roslaunch esvo_core system_rpg.launch
roslaunch esvo_core system_upenn.launch
然后播放 bag 文件作为输入,运行以下指令:
1
roslaunch esvo_time_surface [bag_name].launch
e.g.
1
2
3
roslaunch esvo_time_surface system_hkust.launch
roslaunch esvo_time_surface rpg_bin.launch
roslaunch esvo_time_surface upenn_indoor_flying1.launch
system_hkust有bug 一直不停地 Initialization, 导致程序崩溃 .{: .prompt-warning }
1
2
roslaunch esvo_core system_hkust.launch
roslaunch esvo_time_surface hkust_lab.launch
RPG DATASET
1
2
roslaunch esvo_core system_rpg.launch
roslaunch esvo_time_surface rpg_bin.launch
UPENN DATASET
1
2
roslaunch esvo_core system_upenn.launch
roslaunch esvo_time_surface upenn_indoor_flying1.launch
Code Understanding
ESVO 代码组成如下图所示,主要由三个模块组成,分别是 esvo_time_surface, esvo_Mapping, esvo_Tracking.
- TimeSurface
esvo_time_surface中的TimeSurface实现了 Event Preprocessing 部分,对输入的原始事件流进行滤波,生成 Time-Surface Maps.- esvo_Mapping
esvo_core中的esvo_Mapping实现了 Mapping 部分,接收 Time-Surface,得到深度,生成 Local Map 与 Point Cloud.- esvo_Tracking
esvo_core中的esvo_Tracking实现了 Tracking 部分,对 Local Map 进行跟踪,生成相机的 Pose(6Dof), 将变换矩阵返回给 Mapping 模块- esvo_MVStereo
esvo_core中的esvo_MVStereo实现了 ESVO mapper 部分,以及其他的一些 event-based mapping methods2 3. 作为 multi-view stereo (MVS) pipeline, 该模块需要先验的 pose 作为输入
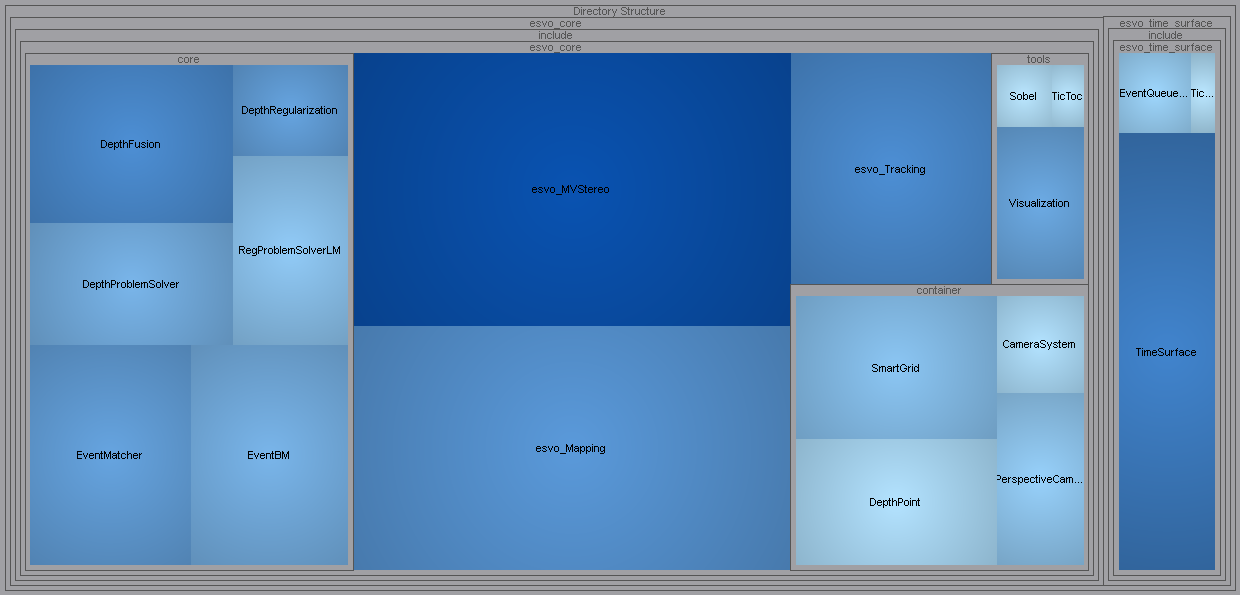 ESVO Treemap from
ESVO Treemap from Scientific Toolworks Understand v6.4
Time-Surface
Time-Surface 是一种将事件流转换为类似于图像帧的数据结构的方法,使得事件流的信息可以用传统的计算机视觉算法处理。Time-Surface 的核心思想是将事件流的时间信息转换为空间信息,将事件流的时间戳 $t_i$ 转换为像素的灰度,这样就可以将事件流转换为图像帧。 本博客在之前已经对 Time-Surface 做了详细的说明,你可以点击这里查看:事件相机图像重构:浅谈Time-Surface
ESVO 中的 Time-Surface 实现在 esvo_time_surface 中,TimeSurface_node.cpp在 ROS 中作为节点运行,TimeSurface.cpp 实现了 Time-Surface 的核心算法以及滤波和校正等功能。 由于水平有限所以在这里只分析单线程的 void TimeSurface::createTimeSurfaceAtTime(const ros::Time& external_sync_time)的实现,多线程的 void TimeSurface::createTimeSurfaceAtTime_hyperthread(const ros::Time& external_sync_time)有待后续解读,但基本原理是相同的。 esvo_time_surface 文件架构如下图所示,TimeSurface_node.cpp 在 ROS 中启动节点,TimeSurface.cpp 实现了主要算法:
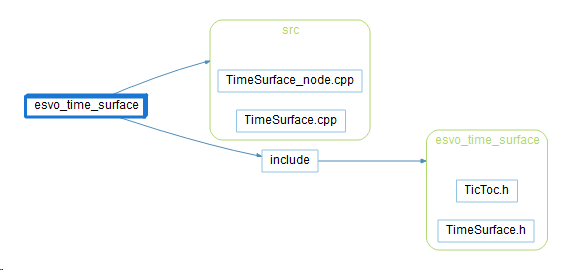 esvo_time_surface architecture from
esvo_time_surface architecture from Scientific Toolworks Understand v6.4
graph LR
subgraph Callback Function
A[TimeSurface::eventsCallback]
B[TimeSurface::cameraInfoCallback]
C[TimeSurface::syncCallback]
end
D[TimeSurface::init]
E[TimeSurface::createTimeSurfaceAtTime]
F[time_surface_pub_]
G[precomputed_rectified_points_]
H[TimeSurface::createTimeSurfaceAtTime_hyperthread]
I[TimeSurface::thread]
A --> D
B --> G
C -->|NUM_THREAD_TS == 1|E
C -->|NUM_THREAD_TS > 1| H
H --> I[TimeSurface::thread]
I --> F[time_surface_pub_]
E --> F
代码主要为两个循环,遍历所有坐标,若 getMostRecentEventBeforeT返回值为真,则将 most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T的时间戳转换为灰度值,赋值给 time_surface_map:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
void TimeSurface::createTimeSurfaceAtTime(const ros::Time& external_sync_time)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(data_mutex_);
if(!bSensorInitialized_ || !bCamInfoAvailable_)
return;
// create exponential-decayed Time Surface map.
const double decay_sec = decay_ms_ / 1000.0;
cv::Mat time_surface_map;
time_surface_map = cv::Mat::zeros(sensor_size_, CV_64F);
// Loop through all coordinates
for(int y=0; y<sensor_size_.height; ++y)
{
for(int x=0; x<sensor_size_.width; ++x)
{
dvs_msgs::Event most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T;
if(pEventQueueMat_->getMostRecentEventBeforeT(x, y, external_sync_time, &most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T))
{
const ros::Time& most_recent_stamp_at_coordXY = most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T.ts;
if(most_recent_stamp_at_coordXY.toSec() > 0)
{
const double dt = (external_sync_time - most_recent_stamp_at_coordXY).toSec();
double polarity = (most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T.polarity) ? 1.0 : -1.0;
double expVal = std::exp(-dt / decay_sec);
if(!ignore_polarity_)
expVal *= polarity;
// Time Surface Mode
// Backward: First Apply exp decay on the raw image plane, then get the value
// at each pixel in the rectified image plane by looking up the
// corresponding one (float coordinates) with bi-linear interpolation.
// Forward: First warp the raw events to the rectified image plane, then
// apply the exp decay on the four neighbouring (involved) pixel coordinate.
// Backward version
if(time_surface_mode_ == BACKWARD)
time_surface_map.at<double>(y,x) = expVal;
// Forward version
if(time_surface_mode_ == FORWARD && bCamInfoAvailable_)
{
// pre-compute the undistorted-rectified look-up table
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1> uv_rect = precomputed_rectified_points_.block<2, 1>(0, y * sensor_size_.width + x);
size_t u_i, v_i;
if(uv_rect(0) >= 0 && uv_rect(1) >= 0)
{
u_i = std::floor(uv_rect(0)); // x coordinate, 下取整
v_i = std::floor(uv_rect(1)); // y coordinate, 下取整
if(u_i + 1 < sensor_size_.width && v_i + 1 < sensor_size_.height) // 防越界
{
// apply the exp decay on the four neighbouring (involved) pixel coordinate
double fu = uv_rect(0) - u_i;
double fv = uv_rect(1) - v_i;
double fu1 = 1.0 - fu;
double fv1 = 1.0 - fv;
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i) += fu1 * fv1 * expVal;
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i + 1) += fu * fv1 * expVal;
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i) += fu1 * fv * expVal;
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i + 1) += fu * fv * expVal;
if(time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i) > 1)
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i) = 1;
if(time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i + 1) > 1)
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i + 1) = 1;
if(time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i) > 1)
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i) = 1;
if(time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i + 1) > 1)
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i + 1) = 1;
}
}
} // forward
}
} // a most recent event is available
}// loop x
}// loop y
// polarity
if(!ignore_polarity_)
time_surface_map = 255.0 * (time_surface_map + 1.0) / 2.0;
else
time_surface_map = 255.0 * time_surface_map;
time_surface_map.convertTo(time_surface_map, CV_8U);
// median blur
if(median_blur_kernel_size_ > 0)
cv::medianBlur(time_surface_map, time_surface_map, 2 * median_blur_kernel_size_ + 1);
// Publish event image
static cv_bridge::CvImage cv_image;
cv_image.encoding = "mono8";
cv_image.image = time_surface_map.clone();
if(time_surface_mode_ == FORWARD && time_surface_pub_.getNumSubscribers() > 0)
{
cv_image.header.stamp = external_sync_time;
time_surface_pub_.publish(cv_image.toImageMsg());
}
if (time_surface_mode_ == BACKWARD && bCamInfoAvailable_ && time_surface_pub_.getNumSubscribers() > 0)
{
cv_bridge::CvImage cv_image2;
cv_image2.encoding = cv_image.encoding;
cv_image2.header.stamp = external_sync_time;
// BACKWARD 在这里进行 rect,矩阵来自于 cameraInfoCallback
cv::remap(cv_image.image, cv_image2.image, undistort_map1_, undistort_map2_, CV_INTER_LINEAR);
time_surface_pub_.publish(cv_image2.toImageMsg());
}
}
Init something
在 TimeSurface::init()中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
void TimeSurface::init(int width, int height)
{
sensor_size_ = cv::Size(width, height);
bSensorInitialized_ = true;
pEventQueueMat_.reset(new EventQueueMat(width, height, max_event_queue_length_));
ROS_INFO("Sensor size: (%d x %d)", sensor_size_.width, sensor_size_.height);
ROS_INFO("Opencv Verison: %s", CV_VERSION);
}
getMostRecentEventBeforeT
函数 getMostRecentEventBeforeT的功能是找到(x,y)处距离现在的时间 t 最近的事件,是较为关键的函数 该函数的作用是找到 [x, y] 处的一系列事件流中最新的一个事件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// 找到距离时间 t 最近的事件
bool getMostRecentEventBeforeT(
const size_t x,
const size_t y,
const ros::Time& t,
dvs_msgs::Event* ev)
{
if(!insideImage(x, y))
return false;
// using EventQueue = std::deque<dvs_msgs::Event>;
// 双向开口的deque,可以从头尾两端进行插入和删除操作
EventQueue& eq = getEventQueue(x, y); // 访问向量中第 x + width_ * y 个元素
if(eq.empty())
return false; // 如果该像素点没有事件,返回false
// 从后往前遍历deque,找到第一个时间戳小于t的事件
// 即找到距离时间 t 最近的事件
for(auto it = eq.rbegin(); it != eq.rend(); ++it)
{
const dvs_msgs::Event& e = *it;
if(e.ts < t)
{
*ev = *it;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
Create Time-Surface
遍历所有坐标,若 getMostRecentEventBeforeT返回值为真,则将 most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T的时间戳转换为灰度值,赋值给 time_surface_map:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// Loop through all coordinates
for(int y=0; y<sensor_size_.height; ++y)
{
for(int x=0; x<sensor_size_.width; ++x)
{
dvs_msgs::Event most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T;
if(pEventQueueMat_->getMostRecentEventBeforeT(x, y, external_sync_time, &most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T))
{
// Time-Surface Implementation
}
}// loop x
}// loop y
Time-Surface 有两种实现方式,Backward version 和 Forward version.
Backward version
Backward version 在事件坐标系下生成的,它直接在事件坐标系下生成 Time-Surface, 不需要相机的内参和外参信息。 从当前时间 t 开始,向前计算,时间戳越近,灰度值越大,即越亮。 公式定义如下所示:
\[\mathcal{T}(\mathbf{x},t)\doteq\exp\left(-\frac{t-t_{\mathsf{last}}(\mathbf{x})}\eta\right)\]其中: $t_last$ 是$(x,y)$处最近(最新)的事件的时间戳,即 most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T.ts $t$ 是当前系统的时间戳,即 external_sync_time
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
const double dt = (external_sync_time - most_recent_stamp_at_coordXY).toSec();
double polarity = (most_recent_event_at_coordXY_before_T.polarity) ? 1.0 : -1.0;
double expVal = std::exp(-dt / decay_sec);
if(!ignore_polarity_)
expVal *= polarity;
// Backward version
if(time_surface_mode_ == BACKWARD)
time_surface_map.at<double>(y,x) = expVal;
Forward version
Forward version 在相机坐标系下生成的,将事件投影到相机的图像平面上,然后在图像平面上生成 Time-Surface. 需要相机的内参和外参信息。 为了加快计算,使用了 look-up table 的方法,将事件投影到相机的图像平面上,然后在图像平面上生成 Time-Surface.
1
2
3
4
5
6
// load look-up table
for (size_t i = 0; i < sensor_size.height * sensor_size.width; i++)
{
precomputed_rectified_points_.col(i) = Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1>(
RectCoordinates(i).x, RectCoordinates(i).y);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// Forward version
if(time_surface_mode_ == FORWARD && bCamInfoAvailable_)
{
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1> uv_rect = precomputed_rectified_points_.block<2, 1>(0, y * sensor_size_.width + x);
size_t u_i, v_i;
if(uv_rect(0) >= 0 && uv_rect(1) >= 0)
{
u_i = std::floor(uv_rect(0)); // x coordinate, 下取整
v_i = std::floor(uv_rect(1)); // y coordinate, 下取整
if(u_i + 1 < sensor_size_.width && v_i + 1 < sensor_size_.height) // 防越界
{
double fu = uv_rect(0) - u_i;
double fv = uv_rect(1) - v_i;
double fu1 = 1.0 - fu;
double fv1 = 1.0 - fv;
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i) += fu1 * fv1 * expVal;
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i + 1) += fu * fv1 * expVal;
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i) += fu1 * fv * expVal;
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i + 1) += fu * fv * expVal;
if(time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i) > 1)
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i) = 1;
if(time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i + 1) > 1)
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i, u_i + 1) = 1;
if(time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i) > 1)
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i) = 1;
if(time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i + 1) > 1)
time_surface_map.at<double>(v_i + 1, u_i + 1) = 1;
}
Mapping
Mapping 部分代码在 esvo_core 中实现, Mapping 的主要功能是接收双目 Time-Surface 以及变换矩阵,计算出带有深度信息的 mapping。 ESVO 提出了一种基于非线性优化衡量事件流时空一致性的目标函数的 mapping 方法。 首先对左右目进行 Block Match,得到左右目的视差图,然后将视差图作为 Nonlinear Optimization and Fusion 的初值,通过非线性优化得到深度图。 在 esvo_core\src\core\esvo_Mapping.cpp 中: 函数调用关系如下所示:
graph LR
A --> F[esvo_Mapping::
InitializationAtTime]
F -->|Yes| B[esvo_Mapping::MappingAtTime]
A[esvo_Mapping::
MappingLoop]
B[esvo_Mapping::
MappingAtTime]
subgraph Nonlinear Optimization and Fusion
E[DepthProblemSolver::solve]
end
subgraph Block Matching
C[esvo_core::core::EventBM::
createMatchProblem]
D[esvo_core::core::EventBM::
match_all_HyperThread]
end
B --> E
B --> C
B --> D
Mapping 初始化 Event Batch Matcher,ebm_ 是一个类对象,它的类型是 EventBM. 构造函数的参数是 ebm_(camSysPtr_, NUM_THREAD_MAPPING, tools::param(pnh_, "SmoothTimeSurface", false)),.
1
2
3
// initialize Event Batch Matcher
ebm_.resetParameters(BM_patch_size_X_, BM_patch_size_Y_, minDisparity, maxDisparity,
BM_step_, BM_ZNCC_Threshold_, BM_bUpDownConfiguration_);
Mapiing 初始化 dpSolver_, 在 esvo_core\include\esvo_core\esvo_Mapping.h 中定义为 DepthProblemSolver dpSolver_; DepthProblemSolver 定义在 esvo_core\include\esvo_core\core\DepthProblemSolver.h
1
dpSolver_(camSysPtr_, dpConfigPtr_, NUMERICAL, NUM_THREAD_MAPPING),
Mapping 中启动了 MappingThread
1
2
3
4
// stereo mapping detached thread
std::thread MappingThread(&esvo_Mapping::MappingLoop, this,
std::move(mapping_thread_promise_), std::move(reset_future_));
MappingThread.detach();
MappingLoop 中调用了 MappingAtTime TS_obs_ 用于传递 Time-Surface, TS_obs_ 的类型是 std::pair<ros::Time, TimeSurface>,其中 TimeSurface 是一个结构体,它包含了一个指向 cv::Mat 的智能指针,以及一个时间戳。
1
std::pair<ros::Time, TimeSurface> TS_obs_;
1
2
3
// Do mapping
if(ESVO_System_Status_ == "WORKING")
MappingAtTime(TS_obs_.first);
InitializationAtTime
系统的初始化使用了 openCV 库中的双目匹配算法 SGBM (Semi-Global Block Matching), SGBM 的参数如下:
这是否导致 ESVO 在某些情况下无法初始化的问题? .{: .prompt-info }
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// SGM parameters (Used by Initialization)
num_disparities_ = 16 * 3;
block_size_ = 11;
P1_ = 8 * 1 * block_size_ * block_size_;
P2_ = 32 * 1 * block_size_ * block_size_;
uniqueness_ratio_ = 11;
sgbm_ = cv::StereoSGBM::create(0, num_disparities_, block_size_, P1_, P2_,
-1, 0, uniqueness_ratio_);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
bool esvo_Mapping::InitializationAtTime(const ros::Time &t)
{
// create a new depth frame
DepthFrame::Ptr depthFramePtr_new = std::make_shared<DepthFrame>(
camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->height_, camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->width_);
depthFramePtr_new->setId(TS_obs_.second.id_);
depthFramePtr_new->setTransformation(TS_obs_.second.tr_);
depthFramePtr_ = depthFramePtr_new;
// call SGM on the current Time Surface observation pair.
cv::Mat dispMap, dispMap8;
sgbm_->compute(TS_obs_.second.cvImagePtr_left_->image, TS_obs_.second.cvImagePtr_right_->image, dispMap);
dispMap.convertTo(dispMap8, CV_8U, 255/(num_disparities_*16.));
// get the event map (binary mask)
cv::Mat edgeMap;
std::vector<std::pair<size_t, size_t> > vEdgeletCoordinates;
createEdgeMask(vEventsPtr_left_SGM_, camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_,
edgeMap, vEdgeletCoordinates, true, 0);
// Apply logical "AND" operation and transfer "disparity" to "invDepth".
std::vector<DepthPoint> vdp_sgm;
vdp_sgm.reserve(vEdgeletCoordinates.size());
double var_SGM = pow(0.001,2);
for(size_t i = 0; i < vEdgeletCoordinates.size(); i++)
{
size_t x = vEdgeletCoordinates[i].first;
size_t y = vEdgeletCoordinates[i].second;
double disp = dispMap.at<short>(y,x) / 16.0;
if(disp < 0)
continue;
DepthPoint dp(x,y);
Eigen::Vector2d p_img(x*1.0,y*1.0);
dp.update_x(p_img);
double invDepth = disp / (camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->P_(0,0) * camSysPtr_->baseline_);
if(invDepth < invDepth_min_range_ || invDepth > invDepth_max_range_)
continue;
Eigen::Vector3d p_cam;
camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->cam2World(p_img, invDepth, p_cam);
dp.update_p_cam(p_cam);
dp.update(invDepth, var_SGM);// assume the statics of the SGM's results are Guassian.
dp.residual() = 0.0;
dp.age() = age_vis_threshold_;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 4, 4> T_world_cam = TS_obs_.second.tr_.getTransformationMatrix();
dp.updatePose(T_world_cam);
vdp_sgm.push_back(dp);
}
LOG(INFO) << "********** Initialization (SGM) returns " << vdp_sgm.size() << " points.";
if(vdp_sgm.size() < INIT_SGM_DP_NUM_Threshold_)
return false;
// push the "masked" SGM results to the depthFrame
dqvDepthPoints_.push_back(vdp_sgm);
dFusor_.naive_propagation(vdp_sgm, depthFramePtr_);
// publish the invDepth map
std::thread tPublishMappingResult(&esvo_Mapping::publishMappingResults, this,
depthFramePtr_->dMap_, depthFramePtr_->T_world_frame_, t);
tPublishMappingResult.detach();
return true;
}
MappingAtTime
初始化新的 DepthFrame, 并将其存储在类成员变量 depthFramePtr_ 中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TicToc tt_mapping;
double t_overall_count = 0;
/************************************************/
/************ set the new DepthFrame ************/
/************************************************/
DepthFrame::Ptr depthFramePtr_new = std::make_shared<DepthFrame>(
camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->height_, camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->width_);
depthFramePtr_new->setId(TS_obs_.second.id_);
depthFramePtr_new->setTransformation(TS_obs_.second.tr_);
depthFramePtr_ = depthFramePtr_new;
DepthFrame 是一个结构体,它代表了一个深度图帧。它包含一个指向 DepthMap 的智能指针,一个 ID,以及一个表示深度图帧在世界坐标系下的变换矩阵。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
struct DepthFrame
{
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
typedef std::shared_ptr<DepthFrame> Ptr;
DepthFrame(size_t row, size_t col)
{
dMap_ = std::make_shared<DepthMap>(row, col);
id_ = 0;
T_world_frame_.setIdentity();
}
void setId(size_t id)
{
id_ = id;
}
void setTransformation(Transformation &T_world_frame)
{
T_world_frame_ = T_world_frame;
}
void clear()
{
dMap_->reset();
id_ = 0;
T_world_frame_.setIdentity();
}
DepthMap::Ptr dMap_;
size_t id_;
Transformation T_world_frame_;
};
vEMP 是用来传递匹配结果的,vEMP 的类型是 std::vector<esvo_core::core::EventMatchPair>
1
std::vector<EventMatchPair> vEMP;// the container that stores the result of BM.
EventMatchPair 结构体定义在 esvo_core\include\esvo_core\container\EventMatchPair.h
其中包含了左右目的事件坐标,时间戳,虚拟视图的变换矩阵,逆深度,匹配代价,梯度,视差等信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
struct EventMatchPair
{
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
EventMatchPair() {}
// raw event coordinate
Eigen::Vector2d x_left_raw_;
// rectified_event coordinate (left, right)
Eigen::Vector2d x_left_, x_right_;
// timestamp
ros::Time t_;
// pose of virtual view (T_world_virtual)
Transformation trans_;
// inverse depth
double invDepth_;
// match cost
double cost_;
// gradient (left)
double gx_, gy_;
// disparity
double disp_;
};
这里通过 ebm_, 调用了 EventBM::createMatchProblem 和 EventBM::match_all_HyperThread,这两个函数的功能是进行 Block Match,得到左右目的视差。 下面对这两个函数进行解读。
1
2
3
4
// block matching
tt_mapping.tic();
ebm_.createMatchProblem(&TS_obs_, &st_map_, &vDenoisedEventsPtr_left_);
ebm_.match_all_HyperThread(vEMP);
CreatMatchProblem
这里定义了一个名为 createMatchProblem的函数,它接受三个参数:StampedTimeSurfaceObs * pStampedTsObs,StampTransformationMap * pSt_map和 std::vector<dvs_msgs::Event *>* pvEventsPtr。在函数内部,它将这些参数存储在类成员变量中,并为每个事件设置了一个视差搜索范围。因此,可以说这个函数创建了一个匹配问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
void esvo_core::core::EventBM::createMatchProblem(
StampedTimeSurfaceObs * pStampedTsObs,
StampTransformationMap * pSt_map,
std::vector<dvs_msgs::Event *>* pvEventsPtr)
{
pStampedTsObs_ = pStampedTsObs;
pSt_map_ = pSt_map;
size_t numEvents = pvEventsPtr->size();
vEventsPtr_.clear();
vEventsPtr_.reserve(numEvents);
vEventsPtr_.insert(vEventsPtr_.end(), pvEventsPtr->begin(), pvEventsPtr->end());
if(bSmoothTS_)
{
if(pStampedTsObs_)
pStampedTsObs_->second.GaussianBlurTS(5);
}
vpDisparitySearchBound_.clear();
vpDisparitySearchBound_.reserve(numEvents);
for(size_t i = 0; i < vEventsPtr_.size(); i++)
vpDisparitySearchBound_.push_back(std::make_pair(min_disparity_, max_disparity_));
}
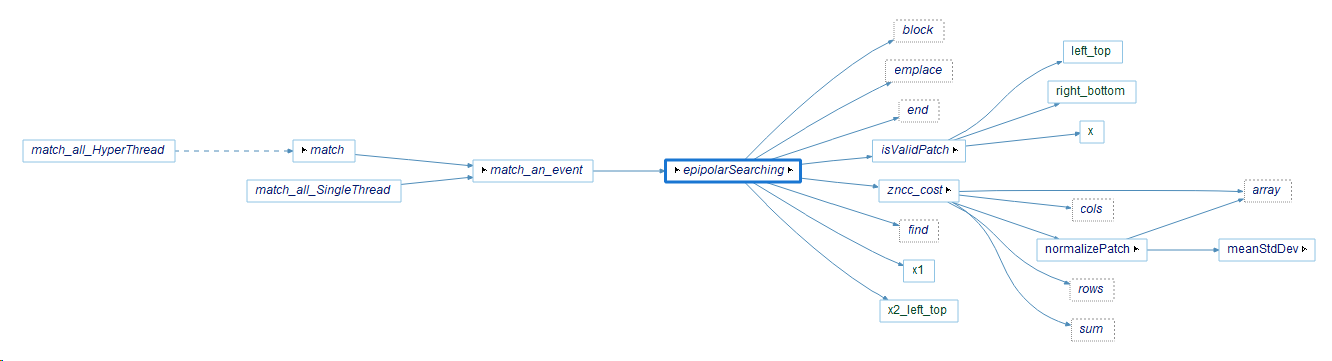
Block Match (match_all_HyperThread)
非线性优化目标函数的使其最小的过程需要初值,ESVO 采用了 ZNCC 块匹配 Block Match 的方法,相较于暴力搜索 Bruteforce Search 更高效。 关于 ZNCC 的原理,本博客在之前已经做了详细的说明,你可以点击这里查看:详解零均值归一化:ZNCC
在 esvo_core\src\core\EventBM.cpp中: 实现了初始化部分求左右目的视差值的代码,函数调用关系如下所示:
全写应为
esvo_core::core::EventBM::match_all_HyperThread,为了排版简写为EventBM::match_all_HyperThread,后续均如此简写。
graph LR
subgraph EventBM
A[match_all_HyperThread]
B[match]
C[match_an_event]
D[epipolarSearching]
E[zncc_cost]
A --> B --> C --> D --> E
end
Match an event
match_an_event 的核心部分如下: match_an_event 以左目作为 src patch,右目作为 dst patch,沿着极线 epipolar 从右向左,计算两者的 ZNCC cost,找到最小的 cost,即为最佳匹配。
在 match_an_event 中 epipolarSearching函数被调用两次,第一次是进行粗略搜索(coarse searching),第二次是进行精细搜索(fine searching)。两者的区别在于搜索的范围和步长不同。
在粗略搜索中,搜索的范围是 lowDisparity到 upDisparity,步长为 step_。而在精细搜索中,搜索的范围是从 bestDisp-(step_-1)到 bestDisp+(step_-1),步长为1。这意味着精细搜索的范围更小,步长更小,因此可以更准确地找到最佳匹配。
总的来说,暴力搜索(coarse searching)是为了快速找到可能的匹配,而精细搜索(fine searching)则是为了更准确地找到最佳匹配。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
bool esvo_core::core::EventBM::match_an_event(
dvs_msgs::Event* pEvent,
std::pair<size_t, size_t>& pDisparityBound,
esvo_core::core::EventMatchPair& emPair)
{
size_t lowDisparity = pDisparityBound.first;
size_t upDisparity = pDisparityBound.second;
// rectify and floor the coordinate
Eigen::Vector2d x_rect = camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->getRectifiedUndistortedCoordinate(pEvent->x, pEvent->y); // x_rect = [u_rect, v_rect]
// check if the rectified and undistorted coordinates are outside the image plane. (Added by Yi Zhou on 12 Jan 2021)
// x_rect(0) is u_rect, x_rect(1) is v_rect
// ---------> u_rect
// |
// |
// |
// ↓
// v_rect
if(x_rect(0) < 0 || x_rect(0) > camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->width_ - 1 ||
x_rect(1) < 0 || x_rect(1) > camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->height_ - 1)
return false;
// This is to avoid depth estimation happening in the mask area.
if(camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->UndistortRectify_mask_(x_rect(1), x_rect(0)) <= 125)
return false;
// x1 in the left time_surface
Eigen::Vector2i x1(std::floor(x_rect(0)), std::floor(x_rect(1)));
Eigen::Vector2i x1_left_top;
if(!isValidPatch(x1, x1_left_top))
return false;
// extract the template patch in the left time_surface
Eigen::MatrixXd patch_src = pStampedTsObs_->second.TS_left_.block(
x1_left_top(1), x1_left_top(0), patch_size_Y_, patch_size_X_);
if((patch_src.array() < 1).count() > 0.95 * patch_src.size())
{
// LOG(INFO) << "Low info-noise-ratio. @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@";
infoNoiseRatioLowNum_++;
return false;
}
// LOG(INFO) << "patch_src is extracted";
// searching along the epipolar line (heading to the left direction)
double min_cost = ZNCC_MAX_;
Eigen::Vector2i bestMatch;
size_t bestDisp;
Eigen::MatrixXd patch_dst = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(patch_size_Y_, patch_size_X_);
// coarse searching
if(!epipolarSearching(min_cost, bestMatch, bestDisp, patch_dst,
lowDisparity, upDisparity, step_,
x1, patch_src, bUpDownConfiguration_))
{
// LOG(INFO) << "Coarse searching fails #################################";
coarseSearchingFailNum_++;
return false;
}
// fine searching
size_t fine_searching_start_pos = bestDisp-(step_-1) >= 0 ? bestDisp-(step_-1) : 0;
if(!epipolarSearching(min_cost, bestMatch, bestDisp, patch_dst,
fine_searching_start_pos, bestDisp+(step_-1), 1,
x1, patch_src, bUpDownConfiguration_))
{
// This indicates the local minima is not surrounded by two neighbors with larger cost,
// This case happens when the best match locates over/outside the boundary of the Time Surface.
fineSearchingFailNum_++;
// LOG(INFO) << "fine searching fails ...............";
return false;
}
// transfer best match to emPair
if(min_cost <= ZNCC_Threshold_)
{
emPair.x_left_raw_ = Eigen::Vector2d((double)pEvent->x, (double)pEvent->y);
emPair.x_left_ = x_rect;
emPair.x_right_ = Eigen::Vector2d((double)bestMatch(0), (double)bestMatch(1)) ;
emPair.t_ = pEvent->ts;
double disparity;
if(bUpDownConfiguration_)
disparity = x1(1) - bestMatch(1);
else
disparity = x1(0) - bestMatch(0);
double depth = camSysPtr_->baseline_ * camSysPtr_->cam_left_ptr_->P_(0,0) / disparity;
auto st_map_iter = tools::StampTransformationMap_lower_bound(*pSt_map_, emPair.t_);
if(st_map_iter == pSt_map_->end())
return false;
emPair.trans_ = st_map_iter->second;
emPair.invDepth_ = 1.0 / depth; // invDepth_ = 1.0 / depth
emPair.cost_ = min_cost;
emPair.disp_ = disparity;
return true;
}
else
{
// LOG(INFO) << "BM fails because: " << min_cost << " > " << ZNCC_Threshold_;
return false;
}
}
Epipolar Searching
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
// patch_src is left patch, patch_dst is right patch
bool esvo_core::core::EventBM::epipolarSearching(
double& min_cost, Eigen::Vector2i& bestMatch, size_t& bestDisp, Eigen::MatrixXd& patch_dst,
size_t searching_start_pos, size_t searching_end_pos, size_t searching_step,
Eigen::Vector2i& x1, Eigen::MatrixXd& patch_src, bool bUpDownConfiguration)
{
bool bFoundOneMatch = false;
std::map<size_t, double> mDispCost;
// searching along the epipolar line (heading to the left direction)
for(size_t disp = searching_start_pos;disp <= searching_end_pos; disp+=searching_step)
{
Eigen::Vector2i x2;
if(!bUpDownConfiguration)
x2 << x1(0) - disp, x1(1); // x2 = [x1(0) - disp, x1(1)]
else
x2 << x1(0), x1(1) - disp; // x2 = [x1(0), x1(1) - disp]
Eigen::Vector2i x2_left_top;
if(!isValidPatch(x2, x2_left_top))
{
mDispCost.emplace(disp, ZNCC_MAX_); // ZNCC_MAX_ = 1.0
continue;
}
// extract the template patch in the right time_surface
patch_dst = pStampedTsObs_->second.TS_right_.block(
x2_left_top(1), x2_left_top(0), patch_size_Y_, patch_size_X_);
double cost = ZNCC_MAX_;
cost = zncc_cost(patch_src, patch_dst, false);
mDispCost.emplace(disp, cost);
if(cost <= min_cost)
{
min_cost = cost;
bestMatch = x2;
bestDisp = disp;
}
// LOG(INFO) << "epipolar searching: " << disp;
}
// 检查在搜索范围内是否存在左右两侧的匹配。
// 如果存在,则检查它们的代价是否小于 ZNCC_MAX_,
// 如果是,则返回 true,表示找到了至少一个匹配。
// 如果不存在,则返回 false,表示没有找到匹配。
if(searching_step > 1)// coarse
{
// mDispCost.end()指向map中不存在的元素
// 确保两端都有匹配
if(mDispCost.find(bestDisp - searching_step) != mDispCost.end() &&
mDispCost.find(bestDisp + searching_step) != mDispCost.end())
{
// 如果两端的匹配成本都小于阈值,则认为找到了一个匹配
if(mDispCost[bestDisp - searching_step] < ZNCC_MAX_ && mDispCost[bestDisp + searching_step] < ZNCC_MAX_ )
if(min_cost < ZNCC_Threshold_)
bFoundOneMatch = true;
// else
// LOG(INFO) << "coarse searching fails: " << mDispCost[bestDisp - searching_step] << " <-> "
// << mDispCost[bestDisp + searching_step];
}
}
else// fine
{
if(min_cost < ZNCC_Threshold_)
bFoundOneMatch = true;
}
return bFoundOneMatch;
}
ZNCC cost
ZNCC cost 公式如下:
$cost = \frac{1}{2}(1 - \frac{\sum_{i,j}(p_l(i,j)-\bar{p_l})(p_r(i,j)-\bar{p_r})}{\sqrt{\sum_{i,j}(p_l(i,j)-\bar{p_l})^2}\sqrt{\sum_{i,j}(p_r(i,j)-\bar{p_r})^2}})$
其中:
$p_l$和$p_r$分别是左右图像上的图像块 $\bar{p_l}$和$\bar{p_r}$分别是它们的均值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
double esvo_core::core::EventBM::zncc_cost(
Eigen::MatrixXd &patch_left,
Eigen::MatrixXd &patch_right,
bool normalized)
{
double cost;
// tools::normalizePatch normalizePatch(Eigen::MatrixXd& patch_src,Eigen::MatrixXd& patch_dst)
// patch_src 中的每个元素减去均值,再除以标准差,得到patch_dst。
if(!normalized)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd patch_left_normalized, patch_right_normalized;
tools::normalizePatch(patch_left, patch_left_normalized);
tools::normalizePatch(patch_right, patch_right_normalized);
cost = 0.5 * (1 - (patch_left_normalized.array() * patch_right_normalized.array()).sum() / (patch_left.rows() * patch_left.cols()));
}
else
cost = 0.5 * (1 - (patch_left.array() * patch_right.array()).sum() / (patch_left.rows() * patch_left.cols()));
return cost;
}
Nonlinear opitmization
在 MappingAtTime中,调用了 DepthProblemSolver::solve, 使用非线性最小二乘法优化目标函数 C,得到最优的逆深度 $\rho^\star$。
1
2
3
4
5
tt_mapping.tic();
// nonlinear opitmization
std::vector<DepthPoint> vdp;
vdp.reserve(vEMP.size());
dpSolver_.solve(&vEMP, &TS_obs_, vdp); // hyper-thread version
DepthPoint 定义在 esvo_core\include\esvo_core\container\DepthPoint.h
SetProblem
这依然是基于窗口,默认值为25,窗口大小会影响匹配精度吗?如果在窗口内出现大的变化,是否会导致匹配失败? .{: .prompt-tip }
esvo_core\src\core\DepthProblem.cpp 中的 DepthProblem::operator() 定义了待优化的目标函数 C:
其中:
残差 residual,表征了左右眼的图像块的差异,残差越小,说明两者越相似,即匹配越准确:
\[r_i(\rho)\doteq\mathcal{T}_{\mathsf{left}}(\mathbf{x}_{1,i},t)-\mathcal{T}_{\mathsf{right}}(\mathbf{x}_{2,i},t)\]$x_1$ 与 $x_2$ 的坐标表示如下:
\[\mathbf{x}_1=\pi\big(^{c_t}\mathbf{T}_{c_{t-\epsilon}}\cdot\pi^{-1}(\mathbf{x},\rho_k)\big)\] \[\mathbf{x}_2=\pi\big(^{\text{right}}\mathbf{T}_{\text{left}}\cdot{}^{c_t}\mathbf{T}_{c_{t-\epsilon}}\cdot\pi^{-1}(\mathbf{x},\rho_k)\big)\]逆深度 inverse depth: $\rho^\star\doteq1/Z^\star $ 相机轨迹 camera trajectory: $T_t−δt:t$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// 将输入向量x作为参数,并计算输出向量fvec
// 优化了DepthProblem类中的operator()函数,
// 该函数的输入是一个VectorXd类型的向量x,输出是一个VectorXd类型的向量fvec。
// 在Levenberg-Marquardt算法中,它将x作为参数输入到operator()函数中,并计算fvec。
// 算法的目标是通过调整x的值来最小化fvec的平方和。
int DepthProblem::operator()( const Eigen::VectorXd &x, Eigen::VectorXd & fvec ) const
{
size_t wx = dpConfigPtr_->patchSize_X_;
size_t wy = dpConfigPtr_->patchSize_Y_;
size_t patchSize = wx * wy;
int numValid = 0;
Eigen::Vector2d x1_s, x2_s;
if(!warping(coordinate_, x(0), vT_left_virtual_[0], x1_s, x2_s))
{
if(strcmp(dpConfigPtr_->LSnorm_.c_str(), "l2") == 0)
for(size_t i = 0; i < patchSize; i++)
fvec[i] = 255;
else if(strcmp(dpConfigPtr_->LSnorm_.c_str(), "zncc") == 0)
for(size_t i = 0; i < patchSize; i++)
fvec[i] = 2 / sqrt(patchSize);
else if(strcmp(dpConfigPtr_->LSnorm_.c_str(), "Tdist") == 0)
for(size_t i = 0; i < patchSize; i++)
{
double residual = 255;
double weight = (dpConfigPtr_->td_nu_ + 1) / (dpConfigPtr_->td_nu_ + std::pow(residual / dpConfigPtr_->td_scale_, 2));
fvec[i] = sqrt(weight) * residual;
}
else
exit(-1);
return numValid;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
void DepthProblem::setProblem(
Eigen::Vector2d & coor,
Eigen::Matrix<double, 4, 4> & T_world_virtual,
StampedTimeSurfaceObs* pStampedTsObs)
{
coordinate_ = coor;
T_world_virtual_ = T_world_virtual;
pStampedTsObs_ = pStampedTsObs;
vT_left_virtual_.clear();
vT_left_virtual_.reserve(1);
Eigen::Matrix<double,4,4> T_left_world = pStampedTsObs_->second.tr_.inverse().getTransformationMatrix();
Eigen::Matrix<double,4,4> T_left_virtual = T_left_world * T_world_virtual_;
vT_left_virtual_.push_back(T_left_virtual.block<3,4>(0,0));
resetNumberValues(dpConfigPtr_->patchSize_X_ * dpConfigPtr_->patchSize_Y_);
}
Problem Solver
graph
A[DepthProblemSolver::
solve]
B[DepthProblemSolver::
solve_multiple_problems]
C[DepthProblemSolver::
solve_single_problem_numerical]
D[DepthProblem::
setProblem]
A --> B --> C
B --> D
Solve Single Problem Numerical
一个使用数值优化求解单个深度估计问题的函数。该函数接受一个初始深度估计、一个指向数值微分对象的指针和一个用于存储优化结果的数组。
在代码中,创建了一个具有一个元素的 Eigen 向量 “x”,它表示初始深度估计。然后创建了一个 Levenberg-Marquardt 优化器,使用数值微分对象进行初始化,并调用 “lm.minimizeInit” 函数以使用初始深度估计初始化优化器。
然后运行优化器,最大迭代次数由 “MAX_ITERATION_” 参数指定。在每次迭代中,调用 “lm.minimizeOneStep” 函数执行一次优化步骤。如果达到最大迭代次数或优化收敛,则终止优化。
优化完成后,将深度估计存储在 “result” 数组中。还计算了估计的方差,使用优化的协方差矩阵进行计算,并将结果存储在 “result” 数组中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
bool DepthProblemSolver::solve_single_problem_numerical(
double d_init, // 初始深度估计
std::shared_ptr< Eigen::NumericalDiff<DepthProblem> > & dProblemPtr, // 数值微分对象指针
double* result) // 存储优化结果的数组指针
{
Eigen::VectorXd x(1); // 创建具有一个元素的 Eigen 向量 x,表示初始深度估计
x << d_init;
// 创建 Levenberg-Marquardt 优化器 lm,使用数值微分对象进行初始化
// 要优化的目标函数是 DepthProblem 类中的 operator() 函数,
// 它计算了当前深度估计下的重投影误差。
// 这个函数的输入是一个深度值,输出是重投影误差。
// 优化器的目标是最小化这个函数的输出,以得到最优的深度估计。
Eigen::LevenbergMarquardt<Eigen::NumericalDiff<DepthProblem>, double> lm(*(dProblemPtr.get()));
lm.resetParameters();
lm.parameters.ftol = 1e-6; // 设置函数值变化的容忍度
lm.parameters.xtol = 1e-6; // 设置参数变化的容忍度
lm.parameters.maxfev = dpConfigPtr_->MAX_ITERATION_ * 3; // 设置最大迭代次数
// 使用初始深度估计初始化优化器
if(lm.minimizeInit(x) == Eigen::LevenbergMarquardtSpace::ImproperInputParameters)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "ImproperInputParameters for LM (Mapping)." << std::endl;
return false;
}
size_t iteration = 0;
int optimizationState = 0;
// 运行优化器,最大迭代次数由 dpConfigPtr_->MAX_ITERATION_ 参数指定
while(true)
{
Eigen::LevenbergMarquardtSpace::Status status = lm.minimizeOneStep(x); // 执行一次优化步骤
iteration++;
if(iteration >= dpConfigPtr_->MAX_ITERATION_)
break;
bool terminate = false;
if(status == 2 || status == 3) // 判断优化状态
{
switch (optimizationState)
{
case 0:
{
optimizationState++;
break;
}
case 1:
{
terminate = true;
break;
}
}
}
if(terminate)
break;
}
// 由于 Eigen 中没有设置参数边界的方法,因此在此应用方便的异常值拒绝方法
if(x(0) <= 0.001) // 如果深度估计小于等于 0.001,则返回 false
return false;
// 更新结果数组
result[0] = x(0);
// 计算方差
Eigen::internal::covar(lm.fjac, lm.permutation.indices());
if(dpConfigPtr_->LSnorm_ == "l2") // 如果使用 L2 范数
{
double fnorm = lm.fvec.blueNorm();
double covfac = fnorm * fnorm / (dProblemPtr->values() - dProblemPtr->inputs());
Eigen::MatrixXd cov = covfac * lm.fjac.topLeftCorner<1,1>();
result[1] = cov(0,0);
}
if(dpConfigPtr_->LSnorm_ == "Tdist") // 如果使用 T 分布
{
Eigen::MatrixXd invSumJtT = lm.fjac.topLeftCorner<1,1>();
result[1] = std::pow(dpConfigPtr_->td_stdvar_,2) * invSumJtT(0,0);
}
result[2] = lm.fnorm * lm.fnorm; // 计算残差平方和
return true;
}
Tracking
TODO: Tracking
Reference
ZHOU Y, GALLEGO G, SHEN S. “Event-based Stereo Visual Odometry,” IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 37(5): 1433-1450, 2021. DOI:10.1109/TRO.2021.3062252. ↩
S.-H. Ieng, J. Carneiro, M. Osswald, and R. Benosman, “Neuromorphic event-based generalized time-based stereovision,” Front. Neurosci., vol. 12, p. 442, 2018. ↩
H. Hirschmuller, “Stereo processing by semiglobal matching and mutual information,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 328–341, Feb. 2008. ↩